Research
How Sponsored Content Affects Consumer Decisions in AI-Powered Retail

PHOTO: JIANG YU. GETTY IMAGES
How does sponsorship disclosure affect consumer trust and behavior in interactions with AI-driven digital sales assistants? Our study highlights the importance of transparency and interactivity in shaping recommendation adherence, providing valuable insights for marketers to balance monetization with trust while also raising awareness for consumers and society about emerging influences.
As consumer expectations for personalized shopping experiences grow – especially among younger, tech-savvy audiences – retailers are facing pressure to seamlessly blend digital and physical touchpoints. One standout innovation in this space is the digital sales assistant (DSA). These AI-powered in-store terminals not only provide tailored recommendations but also simulate humanlike consultations, transforming the shopping journey. While DSAs offer retailers opportunities to drive customer engagement and monetize in-store traffic through retail media, they also raise concerns about consumer trust, particularly around the delivery of sponsored content.
To help address these concerns, this study examines how sponsorship disclosure affects consumer behavior in interactions with DSAs, specifically focusing on recommendation adherence—how likely consumers are to follow product suggestions. We also investigate the role of perceived integrity, which is shaped by the transparency of sponsored content, in infuencing consumer behavior. Additionally, we explore how the level of interactivity in the DSA (from basic to highly engaging) impacts consumer responses to sponsorship disclosure.
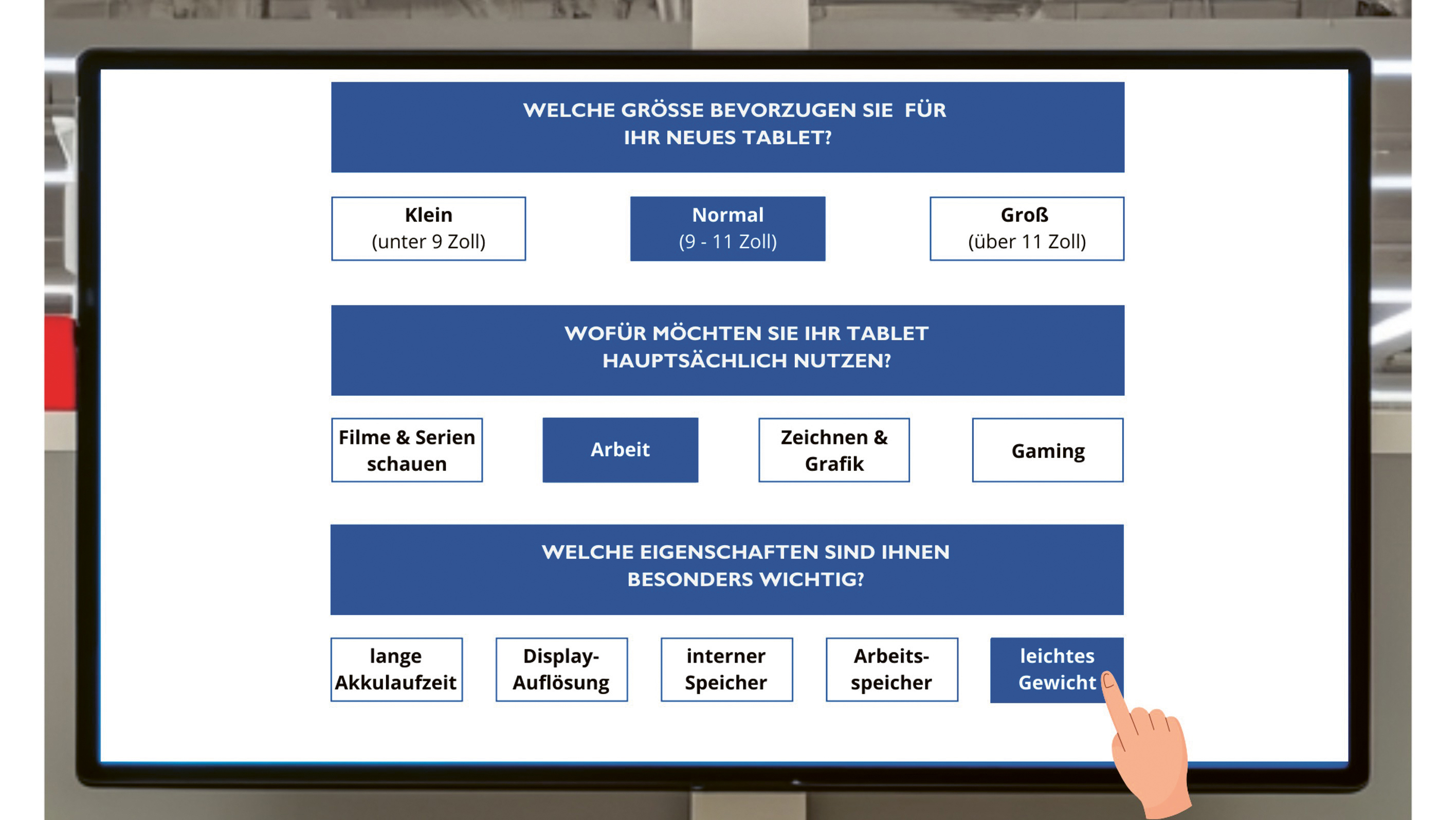
Figure 2: Low-interactivity DSA setting
The Experiment
We conducted an online experiment with 555 participants from Germany, Austria, and Switzerland, using a 2x3 design that varied interactivity (high vs. low) and sponsorship disclosure (baseline, aligned, and divergent). Participants imagined shopping for a tablet and interacted with a DSA in either a high-interactivity condition (an avatar with voice, see Figure 1) or a low-interactivity condition (a simple touchscreen interface, see Figure 2).
After the interaction, participants viewed a product overview where sponsorship disclosure was manipulated. In the baseline condition, only a recommendation label appeared, with no sponsorship information. In the aligned condition, both the “recommended” and “sponsored” labels were placed on the same product (Figure 3). In the divergent condition, the labels appeared on separate products (Figure 4). Participants then selected one of three tablets, allowing us to measure recommendation adherence. Additionally, we assessed perceived integrity and other consumer characteristics to understand the broader impact of sponsorship disclosure and interactivity on consumer behavior.
Results
1. Sponsorship Disclosure and Recommendation Adherence
We found that sponsorship disclosure did not directly affect whether customers followed the product recommendations. This finding suggests that the presence of sponsored content alone does not automatically deter customers from following the DSA’s suggestions.
2. Perceived Integrity and Its Impact on Adherence
However, perceived integrity played a crucial role. When sponsored recommendations were added, participants perceived the DSA as less trustworthy, which lowered their adherence to its recommendations. This result highlights that transparency around sponsorship affects consumer trust and willingness to follow suggestions.
3. Impact of Sponsorship Types (Aligned vs. Divergent)
Contrary to our hypothesis, the analysis showed no significant difference between the aligned and divergent sponsorship types—whether the recommended product is also the sponsored product or different from the sponsored product. This finding suggests that the specific format of sponsorship disclosure does not have as much impact as overall transparency.
4. Interactivity’s Role
Interactivity significantly moderated the effect on perceived integrity. In high-interactivity conditions, the negative impact of sponsorship disclosure on perceived integrity disappeared. This result indicates that engaging, interactive DSAs can mitigate the negative effects of sponsored content on consumer trust.
KEY INSIGHTS
For marketing managers, handling sponsorship disclosure with care is essential. In low-interactivity environments, like basic touchscreen DSAs, transparency becomes even more crucial, as trust can be easily undermined. Retailers should consider alternative monetization strategies, such as offering extended service plans, warranties, or premium memberships, which can generate revenue without jeopardizing consumer trust. Furthermore, transparency is key—clear messaging about how recommendations are generated, along with customer reviews, can help build trust and maintain engagement.
In high-interactivity environments, such as with avatars or humanoid robots, the negative impact of sponsorship disclosures on trust was significantly lower. Retailers can leverage these more engaging experiences to seamlessly integrate sponsored recommendations, aligning with rising consumer expectations for personalized shopping.
For consumers, the rise of AI-driven DSAs offers a more personalized shopping experience, but it also raises the need for greater transparency. With personalized recommendations becoming increasingly common, it’s essential that sponsored content is clearly disclosed to maintain trust and empower consumers to make informed decisions. The study highlights the importance of interactivity—consumers should be aware that in highly interactive settings, they may be more susceptible to the influence of sponsored content. Transparency and awareness are crucial to ensuring a fair and trustworthy shopping experience.
For society, the growing use of sponsored content in both physical and digital retail environments raises important ethical concerns, particularly around consumer autonomy and the transparency of information. In highly interactive settings, where consumers are more engaged, they may not fully recognize the extent to which they are being influenced. This dynamic makes clear sponsorship disclosures even more critical. To help mitigate such effects, regulations should ensure that consumers retain control over their purchasing decisions and can make informed choices without being manipulated by hidden marketing strategies. As these technologies evolve, ensuring consumer protection and autonomy must remain a priority.
Project team
- Dr. Carolin Kaiser, Head of Artificial Intelligence, NIM, carolin.kaiser@nim.org
Cooperation partner
- Prof. Dr. Michael Jungbluth, Technische Hochschule Ingolstadt
- Prof. Patrick Cato, Technische Hochschule Ingolstadt
- Anna Ulrichshofer, Technische Hochschule Ingolstadt
- Lucas Kames, Technical University of Applied Sciences Ingolstadt
Contact




![[Translate to English:] [Translate to English:]](/fileadmin/_processed_/1/2/csm_CK_NIM_01_58bed63910.png)